Prometheus 客户端
启动 Prometheus 客户端。
安装#
go get github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot/v2
go get github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-mux
Prometheus 选项#
| 名字 | 描述 | 类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| mux.prom.enabled | 启动 prometheus | boolean | false |
| mux.prom.path | Prometheus Web 路径 | string | /metrics |
| mux.prom.pusher.enabled | 启动 prometheus pusher | bool | false |
| mux.prom.pusher.jobName | JobName 将会以标签的形式添加到监控指标,并推送到远程 pushgateway | string | "" |
| mux.prom.pusher.remoteAddress | Pushgateway 远程地址, http://x.x.x.x 或者 x.x.x.x | string | "" |
| mux.prom.pusher.intervalMs | 推送间隔(毫秒) | string | 1000 |
| mux.prom.pusher.basicAuth | 远程 Pushgateway 的 Basic auth。 格式:[user:pass] | string | "" |
| mux.prom.pusher.certEntry | rkentry.CertEntry 名称,请参考高级指南 | string | "" |
快速开始#
1.创建 boot.yaml#
---
mux:
- name: greeter
port: 8080
enabled: true
prom:
enabled: true # Optional, default: false
# path: "" # Optional, default: "/metrics"
# pusher:
# enabled: false # Optional, default: false
# jobName: "greeter-pusher" # Required
# remoteAddress: "localhost:9091" # Required
# basicAuth: "user:pass" # Optional, default: ""
# intervalMs: 10000 # Optional, default: 1000
# certEntry: my-cert # Optional, default: "", reference of cert entry declared above
2.创建 main.go#
package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot/v2"
_ "github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-mux/boot"
)
// Application entrance.
func main() {
// Create a new boot instance.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Bootstrap
boot.Bootstrap(context.Background())
// Wait for shutdown sig
boot.WaitForShutdownSig(context.Background())
}
3.验证#
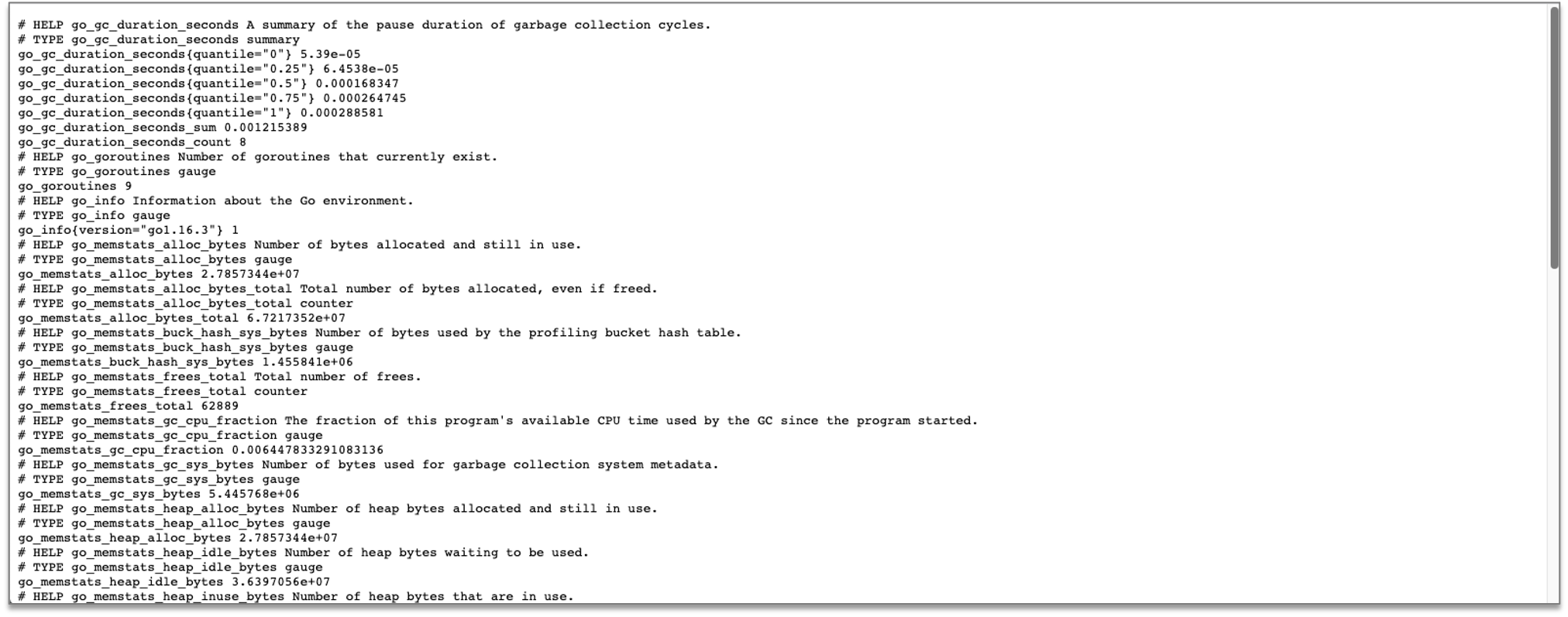
验证
Cheers#
4.Prometheus 客户端中添加监控#
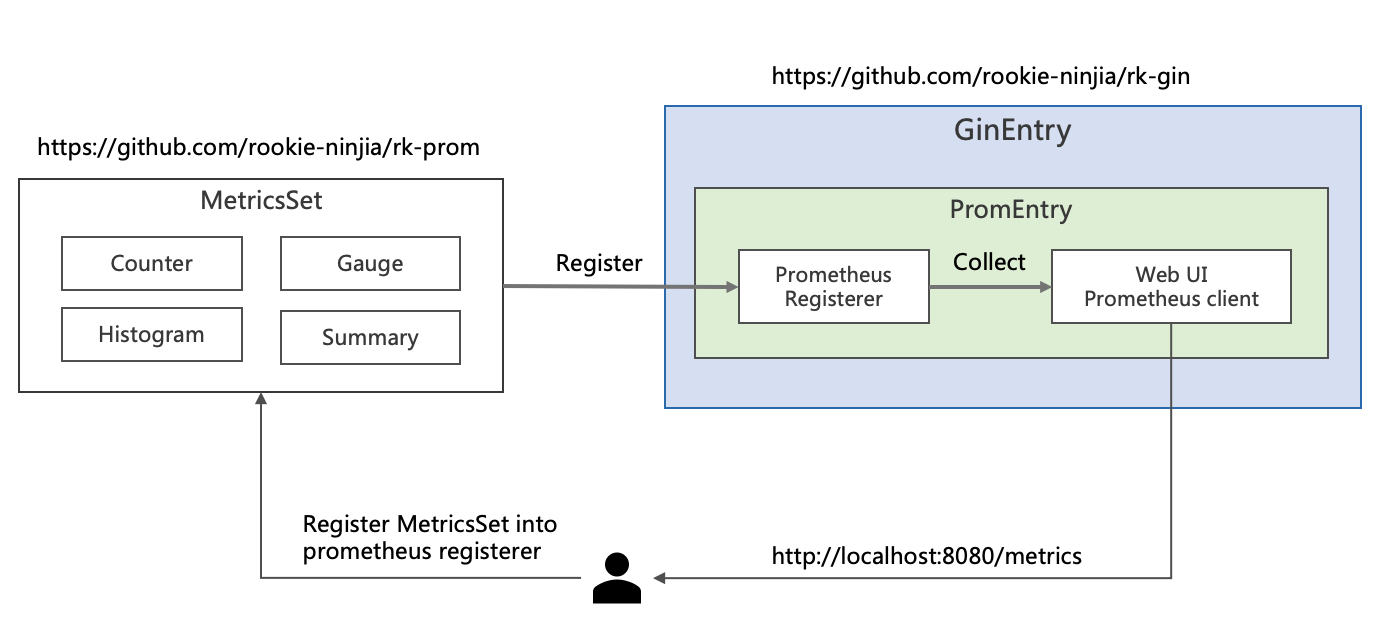
我们需要先了解 Prometheus 中的如下概念。
| 名字 | 详情 |
|---|---|
| MetricsSet | RK 自定义的结构,通过 MetricsSet 注册 Prometheus 的 Counter,Gauge,Histogram 和 Summary |
| Prometheus Registerer | Prometheus 会通过 Registrerer 来管理 Counter,Gauge,Histogram 和 Summary |
| Prometheus Counter | Counter 是一个累积度量,表示单个单调增加的计数器,其值只能增加或重置为零 |
| Prometheus Gauge | Gauge 值可以随意加减 |
| Prometheus Histogram | Histogram 进行采样(通常是请求持续时间或响应大小之类的内容)并将它们计算在可配置的桶中,同时还提供所有观测值的总和 |
| Prometheus Summary | 与 Histogram 类似,摘要样本观察(通常是请求持续时间和响应大小之类的东西) |
| Prometheus Namespace | Prometheus 监控名格式: namespace_subSystem_metricsName |
| Prometheus SubSystem | Prometheus 监控名格式: namespace_subSystem_metricsName |
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-boot/v2"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-entry/v2/middleware/prom"
"github.com/rookie-ninja/rk-mux/boot"
"net/http"
)
// Application entrance.
func main() {
// Create a new boot instance.
boot := rkboot.NewBoot()
// Register handler
entry := rkmux.GetMuxEntry("greeter")
set := rkmidprom.NewMetricsSet("rk", "demo", entry.PromEntry.Registerer)
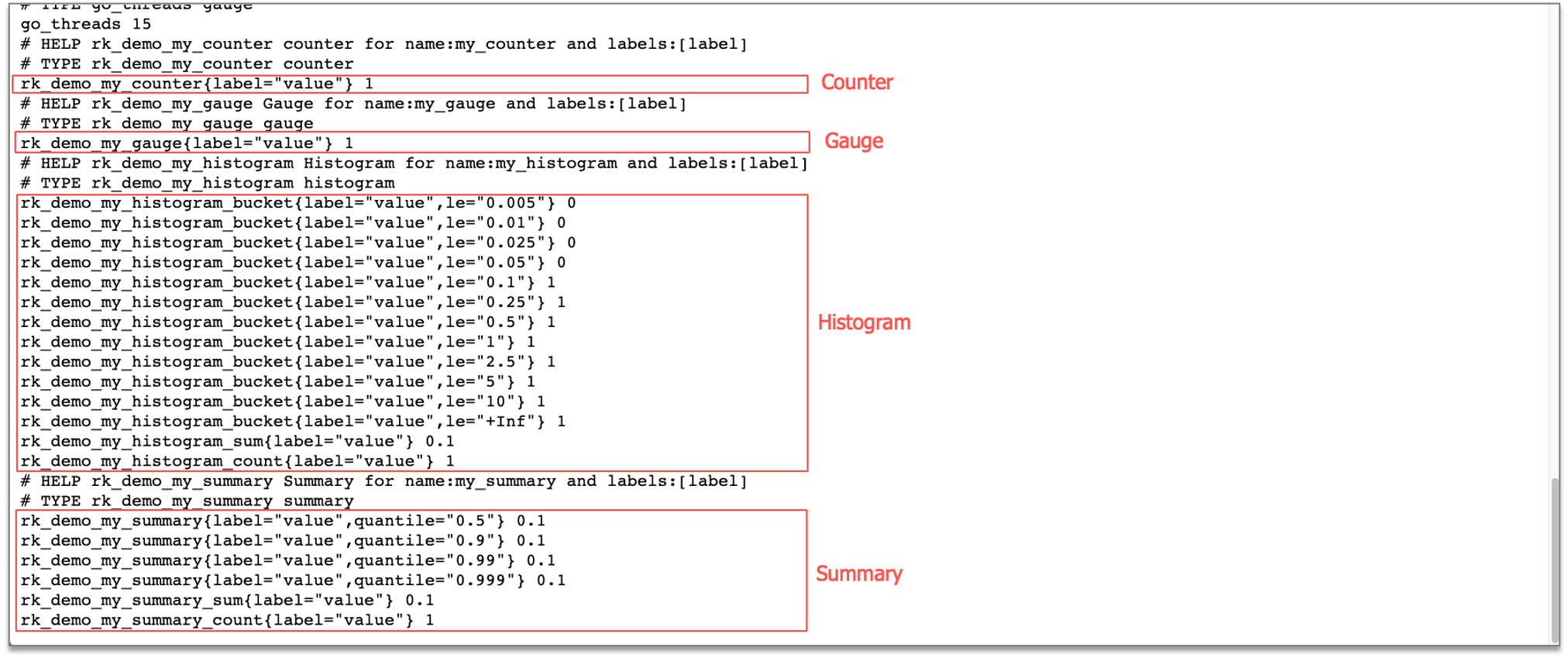
// Register counter, gauge, histogram, summary
set.RegisterCounter("my_counter", "label")
set.RegisterGauge("my_gauge", "label")
set.RegisterHistogram("my_histogram", []float64{}, "label")
set.RegisterSummary("my_summary", rkmidprom.SummaryObjectives, "label")
// Increase counter, gauge, histogram, summary with label value
set.GetCounterWithValues("my_counter", "value").Inc()
set.GetGaugeWithValues("my_gauge", "value").Add(1.0)
set.GetHistogramWithValues("my_histogram", "value").Observe(0.1)
set.GetSummaryWithValues("my_summary", "value").Observe(0.1)
// Bootstrap
boot.Bootstrap(context.TODO())
boot.WaitForShutdownSig(context.TODO())
}
5.验证#
验证
Cheers#
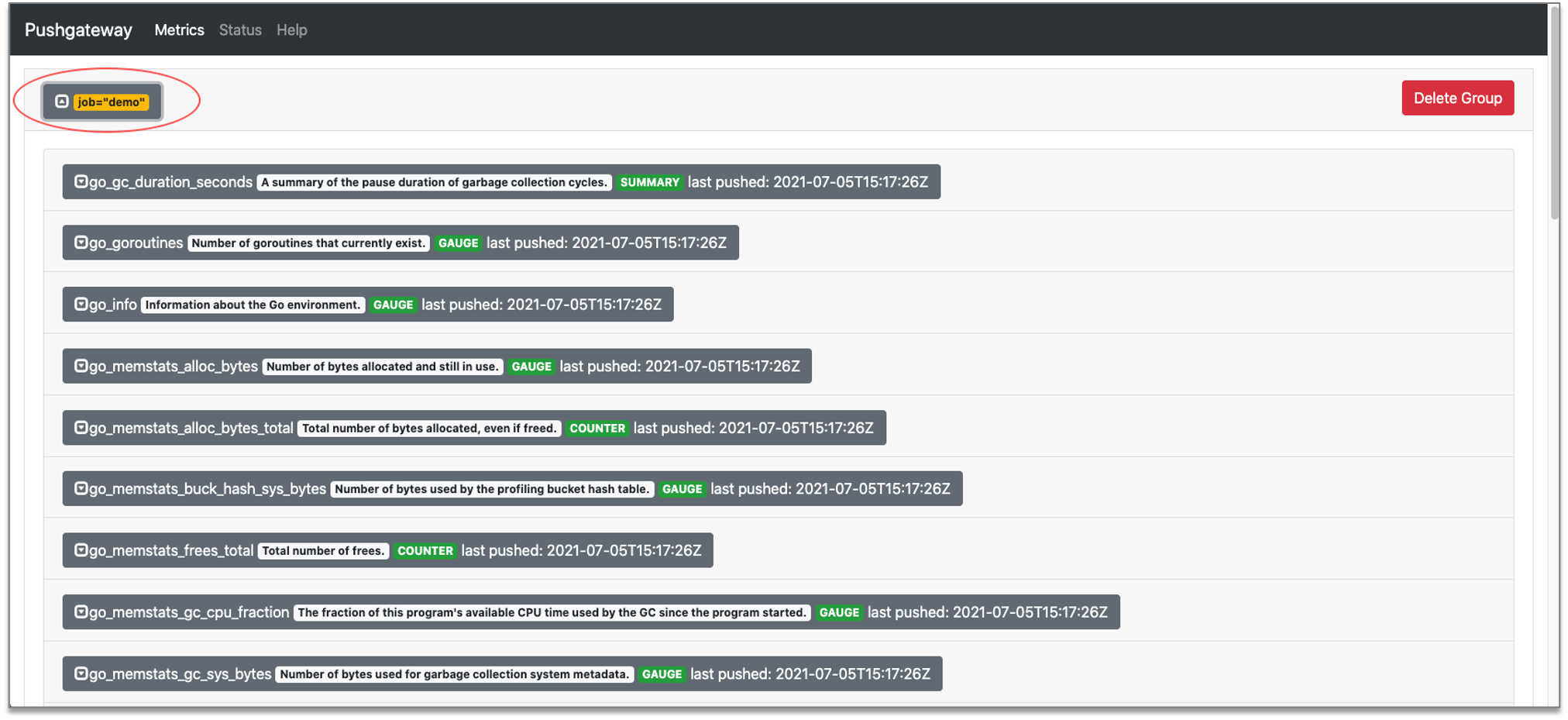
6.推送到 Pushgateway#
在 boot.yaml 中启动 pusher。
---
mux:
- name: greeter
port: 8080
enabled: true
prom:
enabled: true # Optional, default: false
pusher:
enabled : true # Optional, default: false
jobName: "demo" # Required
remoteAddress: "localhost:9091" # Required
intervalMs: 2000 # Optional, default: 1000
# certEntry: my-cert # Optional, default: "", reference of cert entry declared above
在本地启动 pushgateway
$ docker run -p 9091:9091 prom/pushgateway在本地 pushgateway 中验证